GEBRA™ Use Guide: Symptom-driven Update — When Phenotypes Evolve, Your Shortlist Should Too

“My patient’s symptoms changed.”
Familiar story: an infant first presents with developmental delay and hypotonia. Months later, the echo shows dilated cardiomyopathy. In traditional pipelines, that means kicking off a new request, re-uploading a VCF, re-filtering, and waiting—while treatment decisions pause.
Symptom-driven Update was built to remove that lag. Update the phenotype; GEBRA updates the variant ranking—automatically.
What it does

- Edit symptoms (HPO) on the sample page (✏️ icon).
- Save.
- 3ASC immediately reprioritizes variants based on the updated phenotype. No new upload. No manual rebuild of filters. Results refresh in seconds—right in your 3ASC view.
Why it matters: Diagnosis is a moving target. As the phenotype clarifies, your shortlist should, too.
A concrete example of symptom-based update
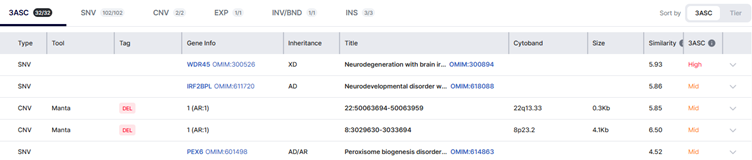
1. Initial phenotype: developmental delay + hypotonia → WDR45 prioritized; PEX6 around rank 5.
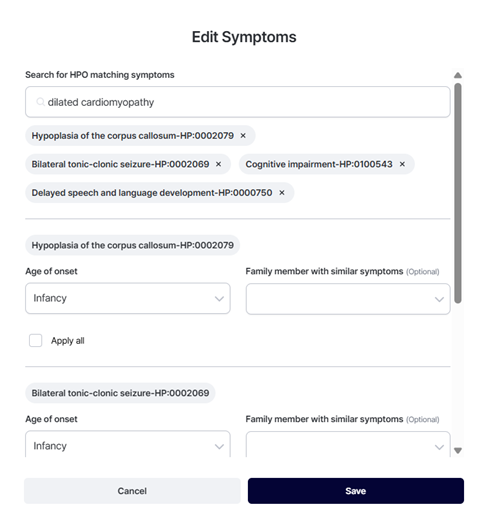
2. Add new symptom: dilated cardiomyopathy.
3. Effect: TTN rises in priority due to phenotype–gene association; the shortlist updates instantly for review.
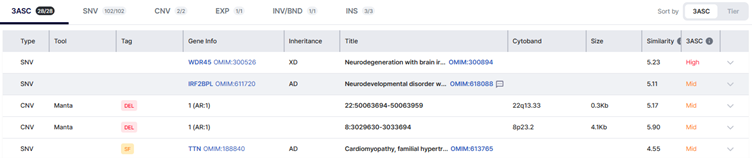
This is not a new end-to-end run; it’s a phenotype-aware reprioritization that brings the most plausible candidates to the top—fast.
The updates you get with one click
When HPO changes, GEBRA recalculates:
- Phenotype–genotype matching (HPO-based)
- Inheritance consistency with the clinical picture
- ACMG/AMP evidence scoring refresh
- False-positive risk signals (e.g., artifact-prone regions)
You get a refreshed, evidence-backed order of candidates while retaining full explainability for boards and reports.
Workflow impact
| Step | Before | With Symptom-driven Update |
| Add/modify symptoms | New analysis request | Inline update on the sample |
| Get updated shortlist | Queue + wait days | Seconds, inside 3ASC |
| Cost | Often additional reanalysis fee | Free within the same sample |
| Explainability | Manual cross-checks | Evidence refreshed alongside rank order |
Result: faster feedback to patients, fewer administrative loops, and an interpretation that keeps pace with the case.
When to use it?
- New clinical features emerge (e.g., seizures, cardiomyopathy, neuropathy).
- Atypical presentations where the initial shortlist doesn’t fully explain the phenotype.
- Follow-up visits where longitudinal data sharpen the clinical picture.
If 3ASC gives you speed, Symptom-driven Update gives you timing—keeping the ranking current each time the phenotype evolves.
It only takes seconds to get started
- Open the sample → click ✏️ Edit symptoms.
- Search/add/remove HPO terms → Save.
- Review the updated High/Mid tiers in 3ASC and proceed to evidence review or reporting.
Pair it with these GEBRA tools 🛠️
- 3ASC: AI-powered prioritization you can trust for a fast, transparent shortlist. (Take a look at 👉 the ‘GEBRA Use Guide : 3ASC.’)
- Filters: If the updated shortlist still feels incomplete, dive into VUS with targeted filters.
- Knowledge Base: Leverage prior cases (VariantsDB/ReportedDB) to see how similar variants behaved across your cohort.
- Gene Coverage: Confirm that critical genes were adequately covered before calling a confident negative.
Learn More
Discover how GEBRA’s integrated interpretation system combines AI and human expertise.
Take a look at all GEBRA™ Related Articles:
- GEBRA™ Use Guide: 3ASC – Finding the One Causal Variant Among Thousands
- GEBRA™ Use Guide: Symptom-driven Update — When Phenotypes Evolve, Your Shortlist Should Too
- GEBRA™ Use Guide: Filters – See What Matters, Faster
- GEBRA™ Use Guide: Knowledge Base – Interpretations That Persist, Diagnoses That Compound
- GEBRA™ Use Guide: Gene Coverage – Diagnostic Confidence Starts with Coverage
- GEBRA™ Use Guide: 3bCNV – From Copy Number Variant Detection to Clinical Interpretation
- GEBRA™ Use Guide: Symptom Color Tag
Get exclusive rare disease updates
from 3billion.

3billion Inc.
3billion is dedicated to creating a world where patients with rare diseases are not neglected in diagnosis and treatment.






