You can see and download 3billion's 4 posters from American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG) 2022 in this page. (Poster Guidelines) If you want to know about our vivid backstory of the conference site interview, please refer to this page.
1. Explicable prioritization of genetic variants by integration of rule-based and deep learning algorithms for diagnosis of rare Mendelian disorders

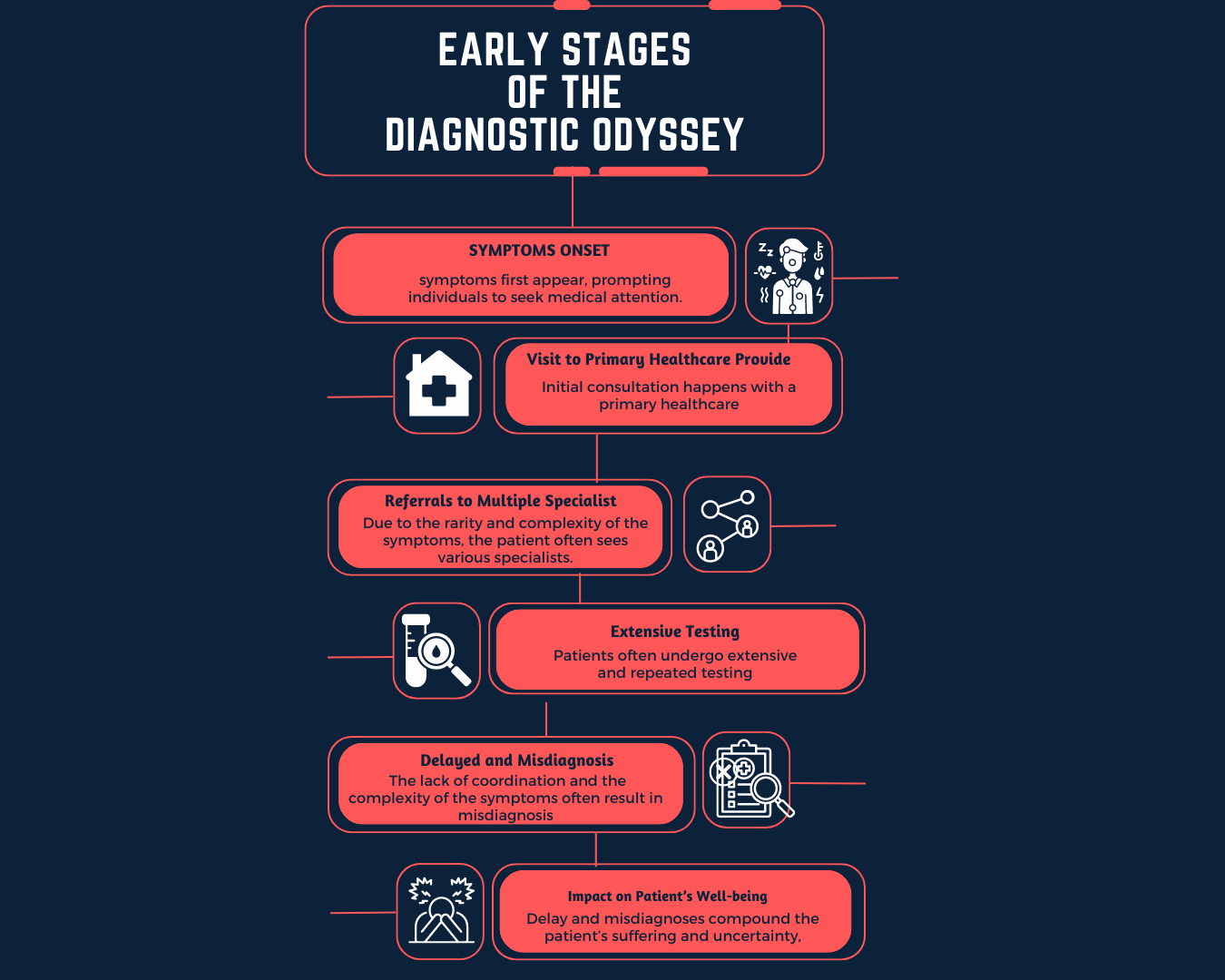
INTROCUCTION
- Using exome, genome and even transcriptome sequencing for making a molecular diagnosis for patients with rare Mendelian disorders has become a common clinical practice. However, determining variant pathogenicity is not a simple task and therefore many variants remain of uncertain significance albeit numerous in silico tools being developed to predict how damaging the variant could be. Here, we report a comprehensive algorithm that prioritizes variants with higher sensitivity than other publicly available tools with added capabilities of annotating variants with the evidence that was used for the prioritization.
- We integrated three different scores into EVIDENCE, an internally developed variant annotation and classification tool. First, the Bayesian score is based on the 28 criteria defined by the ACMG/AMP variant interpretation guidelines. Second, the symptom similarity score quantifies the semantic similarity between the known symptoms of a specific disorder and those observed in the patient. Third, 3Cnet score, generated by a trained deep-learning model, provides the likelihood of a given amino–acid change impacting the protein function.
- The Bayesian score and symptom similarity is used to prioritize variants based on genotype-phenotype knowledge alongside clinical evidences. 3Cnet scores add extra refinement to the variant classification made by the first two scores. We named the overall process of variant prioritization using those scores as 3ASC.
Explicable prioritization ASHG poster 2022Explicable prioritization ASHG poster 2022.pdf 1 MB
2. SpliceVi:a visualization tool for predicting protein consequences based on SpliceAI data

INTRODUCTION
- SpliceAI is an in silico tool that calculates how likely a given single nucleotide variant (SNV) or small insertions and deletions (INDELs) may alter splicing. It outputs Δscores and relative positions from the variant in question for each Δtype [acceptor loss (AL), acceptor gain (AG), donor loss (DL) and donor gain (DG)]. Then, the user has to manually figure out the protein consequences based on the predicted SpliceAI output which can be time-consuming and may result in human error.
- 3billion developed a user-friendly visualizer, SpliceVi, that displays the genomic positions of the Δtype relative to the given variant and provides the predicted protein consequences.
SpliceVi ASHG poster 2022SpliceVi ASHG poster 2022.pdf 3 MB
3. Variant reclassification based on the allele frequency information from exome sequencing data of 20,455 patients enriched with underrepresented populations

INTRODUCTION
- Accurate variant classification is essential for making a molecular diagnosis, and therefore, multiple lines of evidence are carefully considered for determining variant pathogenicity. One of the most important lines of evidence used for diagnosing rare Mendelian disorders is the minor allele frequency (AF) information in the population. Filtering out common variants based on the AF information is the most effective way of narrowing down the number of variants that ened interpretation, as it removes a substantial number of variants that are too common to be disease-causing.
- There are several publicly available databases (DB) such as gnomAD that provide AF information from large populations. Many of these large DBs tend to be dominated by few populations though and therefore it is less effective when filtering out variants for individuals from under-represented populations.
- Here, we investigated how many of our internal variants from 20,455 exomes that are not part of any publicly available DBs can be classified as likely benign (LB), solely based on the AF information from our internal DB but not from gnomAD. A subset of theses variants were present in ClinVar as pathogenic, likely pathogenic or VUS (P/LP/VUS) variants and we were able to downgrade them to likely benign (LB). An internally developed ethnicity prediciting algorithm which estimates ethnicity based on the variant frequency information was used to comfirm that the variants that can be reclassified by this method are indeed from underrepresented populations.
Variant reclassification ASHG poster 2022Variant reclassification ASHG poster 2022.pdf 845 KB
4. A case report of an Egyptian patient with a severe neurodevelopmental disorder and a novel biallelic loss-of-function variant in GOLGA2

INTRODUCTION
- GOLGA2 gene encodes GM130 protein that constitutes Golgi apparatus (GA), which plays a critical role in protein secretion and sorting. The symptoms of various Mendelian disorders associated with the GA component proteins are heterogeneous, but neurodevelopmental phenotype is one of the common phenotypes in relatively severe disorders.
- GOLGA2 gene is not associated with a human disorder yet with only a couple of patients reported with homozygous loss-of-function (LoF) variants.
- Golga2 knockout (KO) mice present with autophagy and fibrosis in lung and liver, and golga2 knocked-down zebrafish show severe skeletal muscle disorganization and microcephaly.