Crohn’s disease | Symptoms, Genetic Testing
About Crohn’s disease

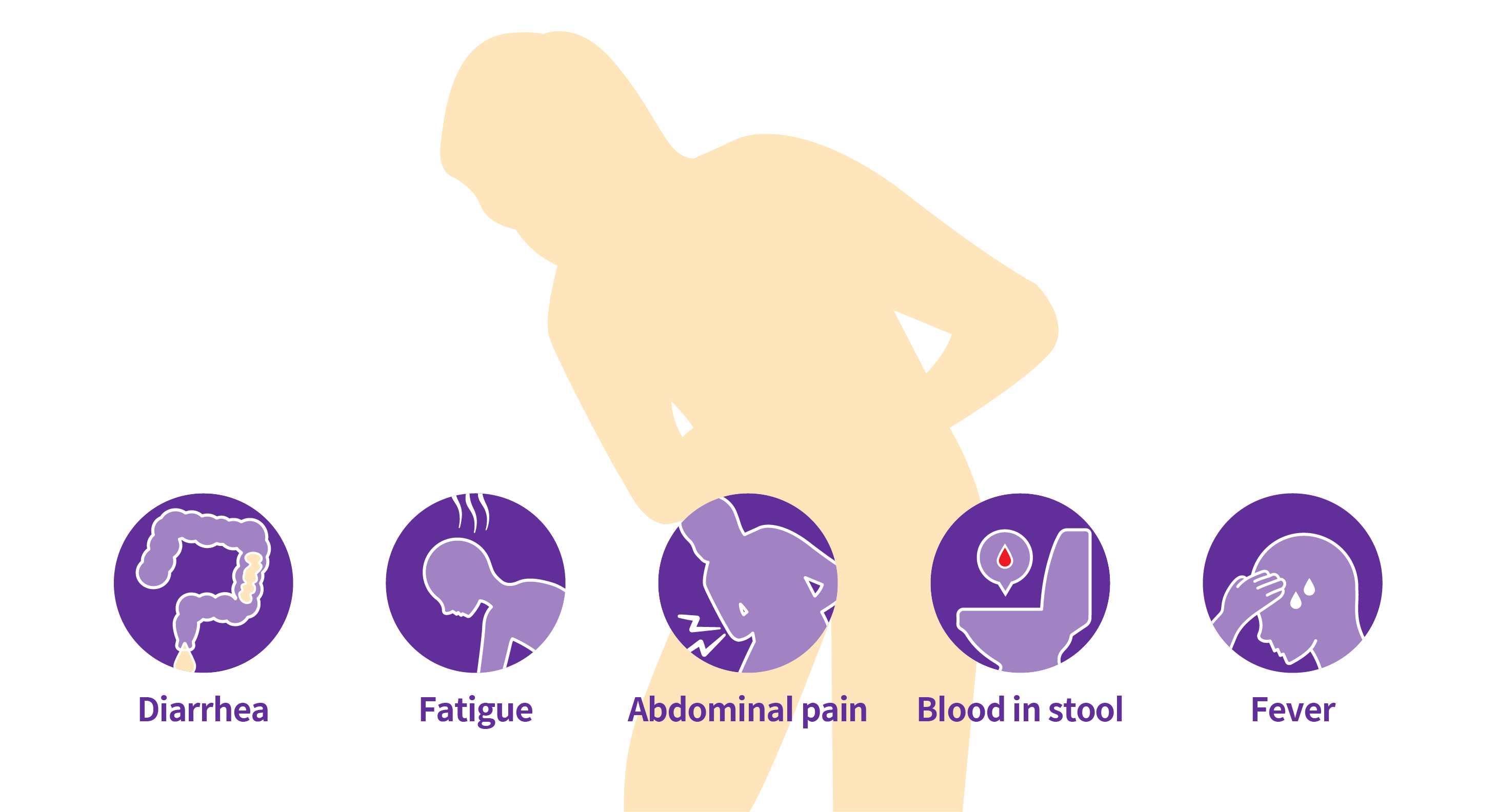
Crohn’s disease is a rare genetic disorder, a well-known type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It is usually characterized by inflammation of the digestive system leading to abdominal pain, diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, and malnutrition.
The cause of Crohn’s disease is complex. By complex, it means that genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors all play some part in causing the disease. Major genes related to Crohn’s disease include NOD2, ATG16L1, IRGM, and IL23R.
Similar to Crohn’s disease, symptoms of monogenic inflammatory bowel diseases usually appear in childhood or adolescence. Therefore, early genetic testing can be helpful for treatments.
PREVALENCE / ONSET

Prevalence
Crohn’s disease affects about 0.1 to 16 cases in 100,000 worldwide.
Onset
The symptoms usually appear between late adolescence and early adulthood.
SYMPTOMS
DIAGNOSIS
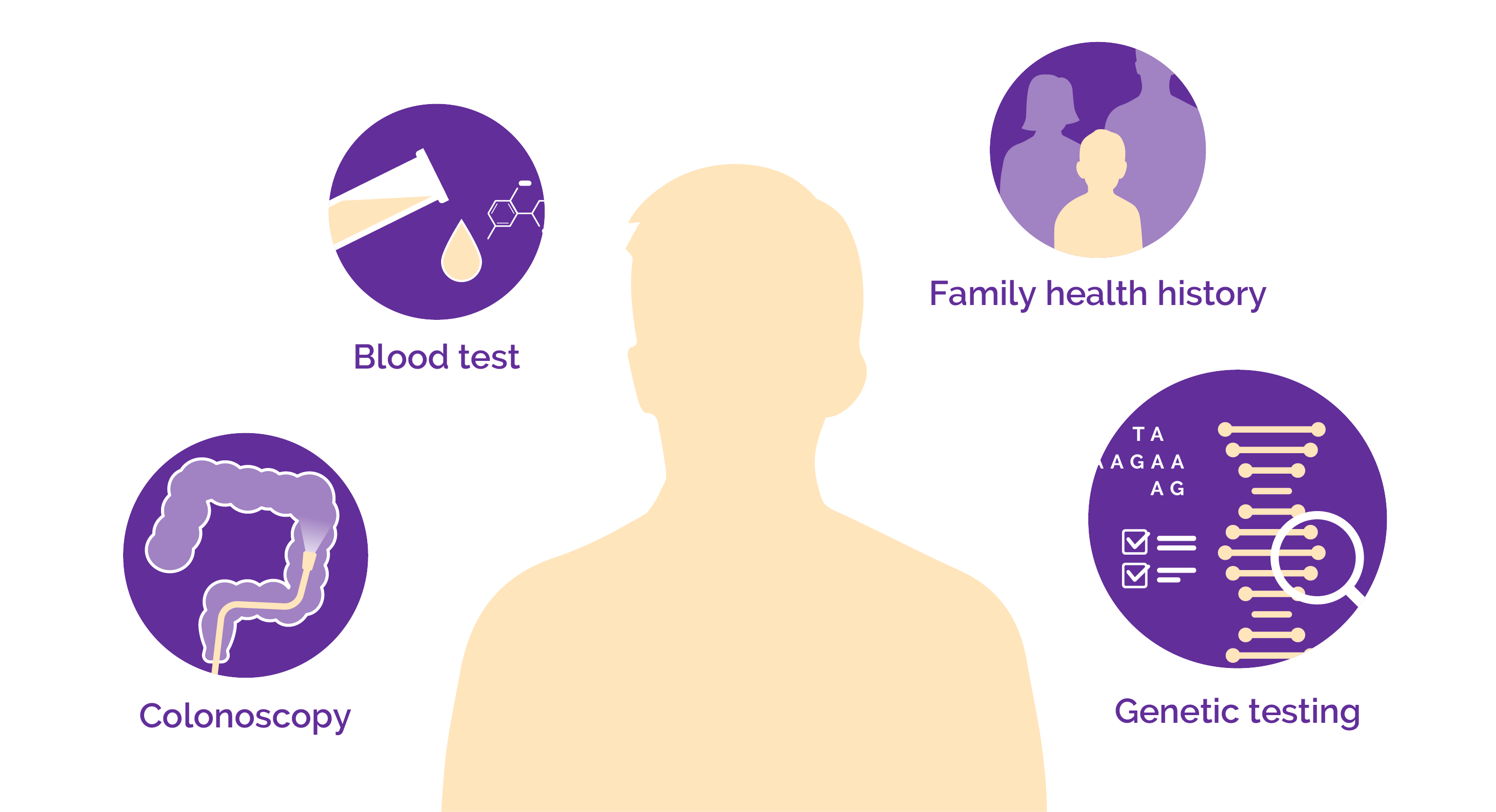
Since Crohn’s disease shares many symptoms with other diseases, there is no single test to diagnose Crohn’s disease. There will be multiple tests to rule out other diseases and make a final diagnosis.
Physical exam, family health history, and blood test to check the inflammation level can be held first. Colonoscopy could also be conducted, and genetic testing can be necessary to reveal its genetic background.
In particular, symptoms of monogenic IBD diseases, including some of Crohn’s disease, are usually present from childhood or adolescence. Therefore, early genetic testing can be helpful for quick diagnosis and treatment to avoid a long diagnostic odyssey.
To read more about a patient’s IPEX syndrome diagnosis story that shares similar symptoms to Crohn’s disease, read James’ diagnosis story of diagnosing IPEX syndrome here.

What Makes Our Exome Testing Advanced?
Find out how our enhanced exome solutions deliver better coverage and accuracy.
INHERITANCE PATTERN
Genetics plays a role in Crohn’s disease, but environmental and lifestyle factors also play a part. About 15% of Crohn’s disease patients have first-degree family members who are also suffering from the disease.
So far, there is no single treatment that fits all patients with Crohn’s disease. The goal of medical treatment is mostly to manage the symptoms, usually to reduce inflammation.
Anti-inflammatory drugs such as Corticosteroids and oral 5-aminosalicylates are often used to achieve the goal. Immune system suppressors, biologics, antibiotics are also often used to treat inflammation.
TREATMENTS
So far, there is no single treatment that fits all patients with Crohn’s disease. The goal of medical treatment is mostly to manage the symptoms, usually to reduce inflammation.
Anti-inflammatory drugs such as Corticosteroids and oral 5-aminosalicylates are often used to achieve the goal. Immune system suppressors, biologics, antibiotics are also often used to treat inflammation.
Get exclusive rare disease updates
from 3billion.

Jane Han
Sales and business development professional in healthcare, expanding market share, managing key partnerships, and driving sales growth in the healthcare sector.