The Role of Genetic Testing in Clinical Trials: Advancing Rare Disease Research

Many clinicians are looking for the right type of genetic testing and the company for their clinical trials. There are a lot of genetic testing companies and labs around the world, and they all say they are the best choice, but that’s not true. Depending on the characteristics of the clinical trial, the most efficient test should vary. Today, let’s talk about how to successfully complete your clinical trial from a genetic testing perspective.
Genetic testing in clinical trials
Genetic testing in clinical trials refers to the process of analyzing an individual’s DNA to identify specific genetic variants that may be relevant to the study. It involves various techniques such as DNA sequencing, genotyping, or other molecular biology methods to examine the genetic information of participants.
What types of genetic testing are used in clinical trials?
Physician or geneticist should be aware of different types of genetic testing, such as targeted gene panel testing, whole exome sequencing (WES), whole genome sequencing (WGS), chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA), and so on.
More recently than in the past, WES and WGS are often used in clinical research due to the accessibility of increasingly comprehensive and highly diagnostic testing.
What are the potential benefits of genetic testing in clinical trials?
Genetic testing in clinical trials serves several purposes. It can help identify individuals who have specific genetic variations that make them eligible for a particular trial. It can also be used to stratify participants based on their genetic characteristics, enabling researchers to study the impact of genetic variations on treatment response or disease progression. Additionally, genetic testing may be conducted to assess the safety and efficacy of investigational drugs in specific subpopulations with genetic predispositions.
It is typically carried out by trained laboratory professionals or geneticists who specialize in molecular genetics. The testing may be conducted within the clinical site or outsourced to specialized laboratories that have the necessary infrastructure and expertise.
Some researchers prefer to use only labs or companies that are close and affordable. But that may not be a good choice. Genetic testing can vary in turnaround time, price, and even results depending on the equipment and expertise available and how optimised the process is.
What is difference between a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA)-approved laboratory vs a research laboratory?

A CLIA-approved laboratory is specifically designed to provide clinical testing services for patient care. These laboratories are regulated by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) in the United States.
CLIA-approved laboratories must comply with rigorous quality control standards and undergo accreditation to demonstrate their proficiency and reliability. Research laboratories may have their own quality control measures but may not require the same level of accreditation for their research purposes.
It’s important to note that some laboratories can have both clinical and research components, conducting both clinical testing and research activities. In such cases, the laboratory may need to meet the regulatory requirements for both CLIA certification and research oversight.
What are the benefits of using 3billion vs other lab providers?
3billion provides end-to-end services for clinical trials. From sample accession to results delivery, we provide the high diagnosis rates services you need for successful research, along with broad coverage, clear clinical-level reports, and the data you need. (VCF & FASTQ) These options are also free.


Once a sample is received at 3billion for WES or WGS, what happens next?
After the patient’s sample is collected, 3billion extracts DNA from the sample to create genetic data. And then, 3billion’s variant interpretation system lists pathogenic variant candidates after analyzing them. 3billion’s medical genetics division will confirm the top 1~2 variants that best explain the patient’s phenotypes and provide clinical report to physicians. Of course, physicians can always consult with our medical geneticists about the results. Those cases with no pathogenic variants found will be reanalyzed daily with 3billion’s reanalysis pipeline.
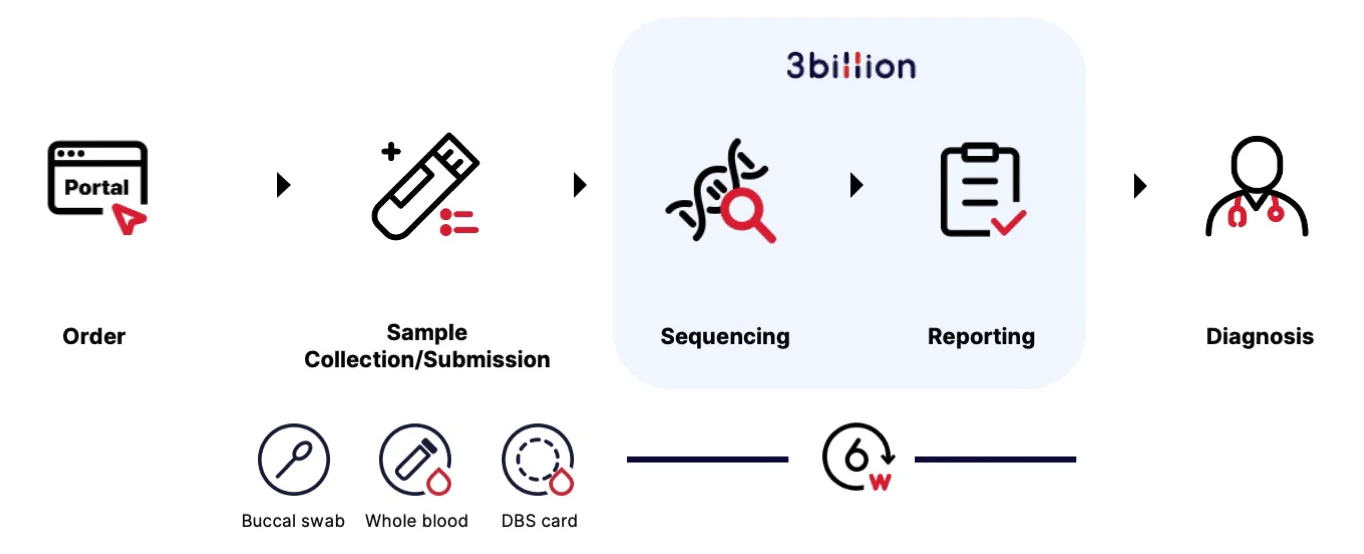
Check if we can provide you with the most reasonable options for your research!
Get exclusive rare disease updates
from 3billion.

Sree Ramya Gunukula
Marketing Leader with experience in the pharma and healthcare sectors, specializing in digital health, genetic testing, and rare disease diagnostics.







