Best Practices for Medical Staff to Accurately Diagnose Rare diseases
Diagnosing rare genetic diseases presents unique challenges due to the complexity and variability of symptoms. Accurate diagnosis is critical for effective treatment and management. Here are some best practices for medical staff to enhance the accuracy of diagnosing these conditions.
1. In-Depth Symptom Observation
Thoroughly observing and documenting a patient’s symptoms is crucial. Detailed information about the onset, duration, and progression of symptoms can provide essential clues for diagnosis. Medical staff should:
• Conduct comprehensive patient interviews.
• Record detailed family medical histories.
• Utilize standardized symptom checklists
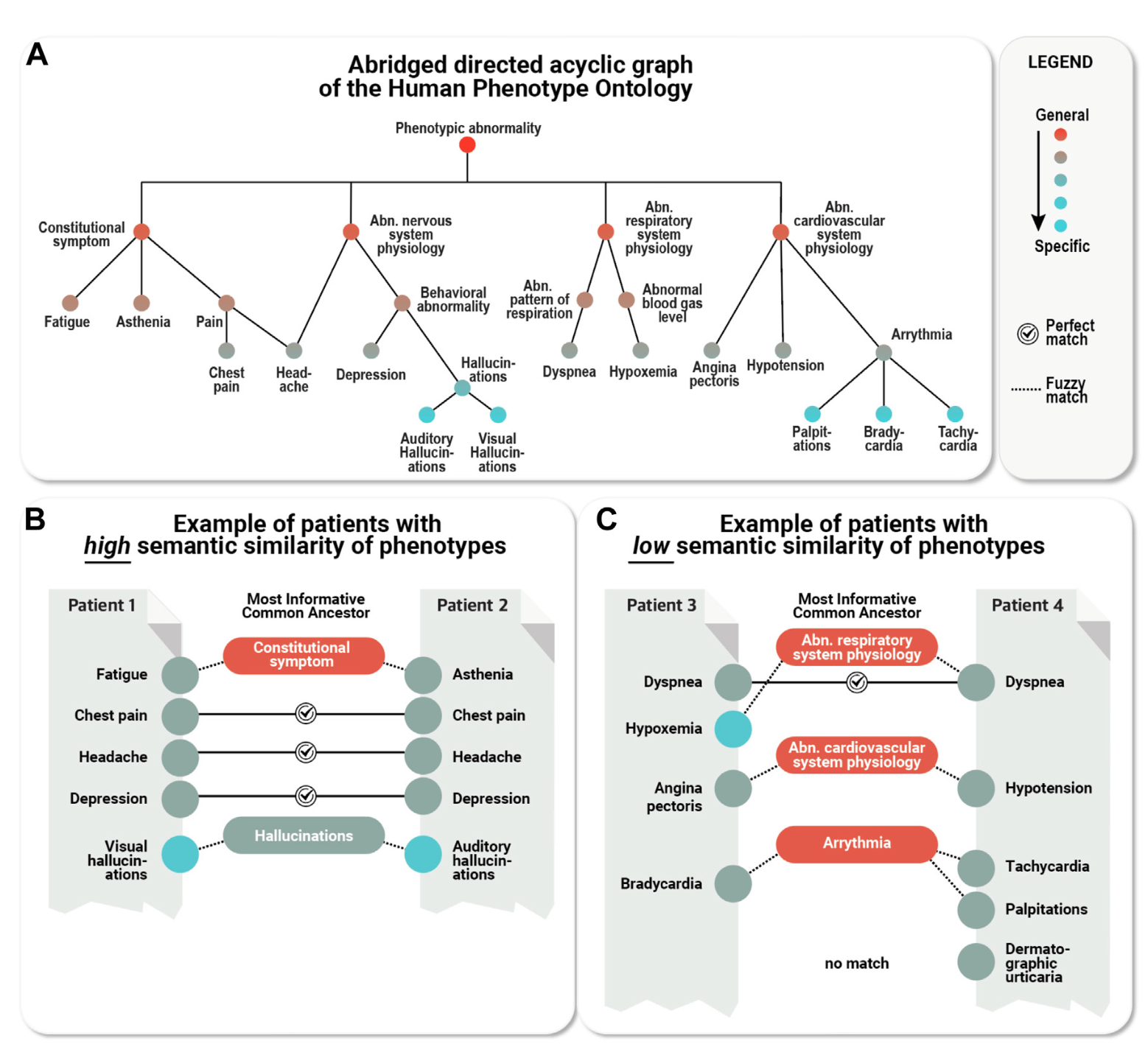
The more diverse the information and the more specific the symptoms, the higher the likelihood of diagnosis. Rare disease diagnosis is made by selecting pathogenic mutations that are highly correlated with the patient’s symptoms. The lower the depth of symptom information provided by medical staff to testing agencies, the more difficult it is to accurately measure disease similarity.
The Figure below illustrates the importance of the specificity of HPO (Human Phenotype Ontology) term symptom similarity calculation. In another example, “Dyspnea” and “Hypoxemia” are related but not identical terms. Their similarity is assessed based on their common ancestor “Respiratory system symptom”, demonstrating how detailed symptom information helps in creating a precise match.
2. Collaboration and Multidisciplinary Approach
Collaborating with specialists from different fields ensures a holistic approach to diagnosis. Geneticists, neurologists, and other specialists can provide insights that might be overlooked in a single-discipline approach. Regular case meetings and collaborative platforms can facilitate this multidisciplinary engagement.
3. Selecting the Right Genetic Testing Agencies
In the diagnosis of rare diseases, the application of advanced diagnostic tools is essential. These tools include genetic testing, biochemical tests, and imaging studies, each playing a crucial role in identifying the underlying causes of these complex conditions. The sequencing techniques are instrumental in diagnosing genetic disorders, especially when the clinical presentation is ambiguous or when traditional diagnostic methods have failed.
What is more important is, choosing an organization that continuously updates its databases and reanalyzes data is essential. For example, 3billion updates all its databases every night at 11 pm with the most up-to-date information. This process is linked to a reanalysis system for undiagnosed patients, continuously providing new diagnostic results. This practice ensures that the latest information is always utilized in the diagnostic process, improving the accuracy and speed of rare disease diagnoses.
3Billion has incorporated an automated daily reanalysis service in all its Whole Exome Sequencing services. This service automatically reanalyzes data for cases where initial results were uncertain or negative, using updated information daily. Over five years, this approach has led to meaningful updates in the diagnoses of about 1-2% of all tested patients receiving additional diagnoses through reanalysis.
Are you curious about the results of 3Billion’s reanalysis? You can read the full article here.
4. Staying Informed and Continuing Education
To stay informed and continue their education, medical staff should regularly review the latest research and updates in genetics. Attending relevant medical conferences and workshops is crucial for keeping abreast of new developments and networking with experts in the field. Utilizing online databases and resources such as OMIM and GeneReviews provides access to comprehensive information on genetic disorders and emerging diagnostic techniques. By integrating these practices, healthcare professionals can maintain a high level of knowledge and competency in diagnosing and managing rare genetic diseases.
Conclusion
In the field of rare disease diagnosis, the depth and specificity of symptom information provided by medical staff play a critical role in the accuracy of diagnoses. Continuous monitoring and detailed symptom recording increase the chances of identifying the correct pathogenic mutations. Moreover, partnering with organizations that continuously update and reanalyze data ensures that the latest information is always used in the diagnostic process, improving outcomes for patients with rare diseases.
3billion is your partner in navigating the genomic landscape, providing optimized genetic testing services and non-stop reanalysis to keep you at the forefront of genetic research and diagnosis. Don’t miss out on our tailored solutions—get an affordable quote today and decide at your convenience.
Get exclusive rare disease updates
from 3billion.

Sree Ramya Gunukula
Marketing Leader with experience in the pharma and healthcare sectors, specializing in digital health, genetic testing, and rare disease diagnostics.







