3Cnet
AI Pathogenicity Prediction Tool built on 3Cs: Clinical Data, Common Variants, Conservation DataWhy do we need a pathogenicity prediction tool?
When a patient’s genetic information is analyzed using whole exome sequencing (WES), about 100,000 genetic variants are found. Millions of genetic variants are found with whole genome sequencing (WGS). However, for the majority of detected variants, it is difficult to determine whether the variant is disease-causing.
Pathogenicity prediction provides additional evidence for variant interpretation. To streamline this process, several prediction tools using AI technology have been developed and are utilized in the market.
3billion has developed 3Cnet, which shows more robust variant pathogenicity prediction and classification performance compared to currently available tools on the market. 3billion applies this powerful prediction tool to streamline accelerate diagnosis.
3Cnet, which has recently been updated to version 2, has expanded the types of variants that can be evaluated, including start-loss, stop-gain, stop-loss, in-frame deletion, frameshift, in-frame insertion, delins, duplication, 5' extension, and 3' extension. It is now possible to predict the pathogenicity of 99.99% of variants.
What makes 3Cnet different?
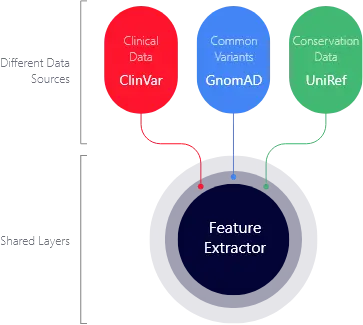
constraints from UniRef database
Information on pathogenic and benign variants from ClinVar database
Information on common variants from GnomAD database
Information on variants reflecting evolutionary
3Cnet learns from three types of data to minimize bias: clinical data, common variant data, and conservation data. 3Cnet’s sensitivity is 2.2 times higher than that of other variant pathogenicity prediction tools.
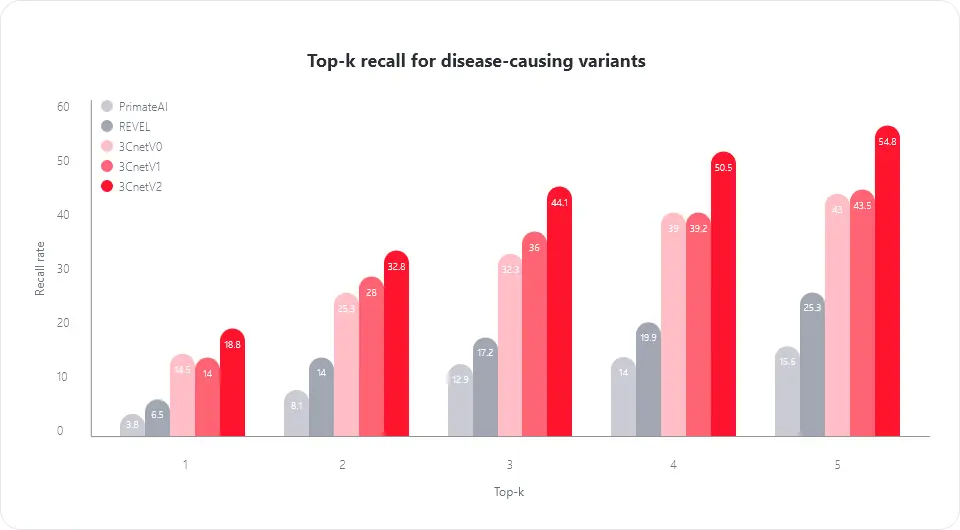

*Top-k recall shows each prediction tool’s probability of determining the correct disease-causing variant among the top-ranked variants.
What are the advantages of 3Cnet?
3Cnet helps the variant interpretation process by predicting the pathogenicity of variants with insufficient evidence.
3Cnet has higher sensitivity compared to other pathogenicity prediction tools, so new evidence that has not been revealed can be added. Through this technology, variants identified as VUS are more likely to be reclassified as pathogenic/likely pathogentic.















